It is also formed in the seeds during germination. Types of glycosidic bonds If glycosidic oxygen associated with aglycone or lowering end sugar it really is known as as O-glycosidic bonds.
Glycosidic Bond The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki
Glycosidic bonds are the covalent bonds that occur between sugars carbohydrates and other molecules which can be other monosaccharides or other molecules of various nature.

. A type of covalent bond that joins two carbohydrate molecules. A substance containing a glycosidic bond is termed a glycoside. Which of the following molecules act as building blocks monomers of polypeptides.
We can see that glycosidic linkage is ROR linkage which is an ether linkage. These sugar chains of monosaccharides are able to form further glycosidic bonds with alcohols and amines to produce sugar acetalsglycosides and nucleosides. A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate sugar molecule to another group which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond formed between two carbohydrate molecules or a carbohydrate and another a molecule that may not be a carbohydrate. The O-glycosidic linkage is found in all oligosaccharides like sucrose maltose maltotriose etc. Formation of ethyl glucoside.
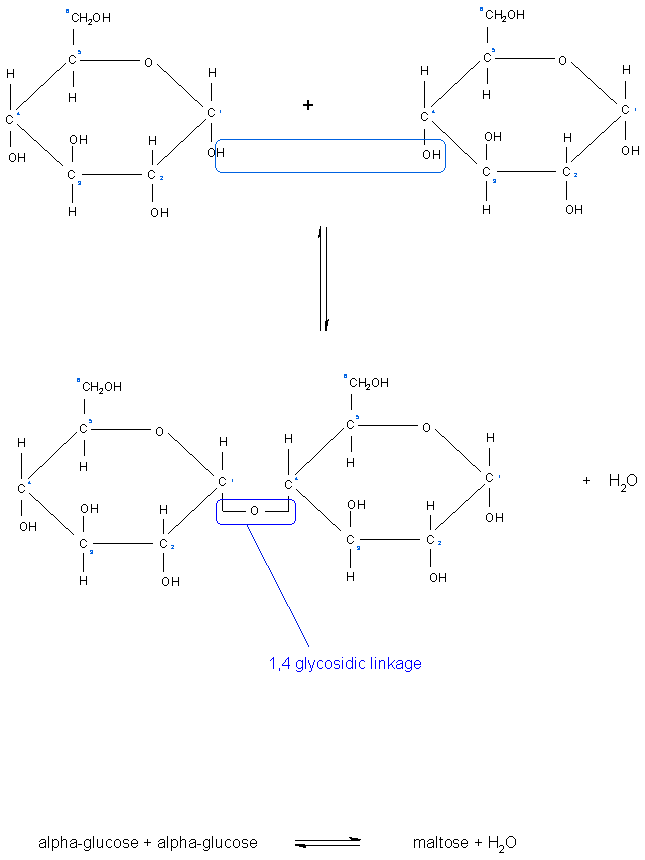
Glycosidic linkage occurs between the molecules of two monosaccharides through an oxygen atom and is accompanied by the loss of water molecule. Sign in to download full-size image. Glycosidic bond is formed normally between carbon atoms 1 and 4 of neighbouring monosaccharide units.
Glycosidic bonds join monosaccharides or longer sugar chains to other carbohydrates forming disaccharides oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. 14 alpha glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH on the carbon-1 is below the glucose. This bond is a β-glycosidic linkage between N-acetylgalactosamine and the hydroxyl group of either serine or threonine.
Glycosidic linkage is the type of linkage between adjacent glycosylation on the main chain of polysaccharides 114. A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate sugar molecule to another group which may or may not be another carbohydrate. A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate sugar molecule to another group which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
A glycosidic bond is a covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate to another functional group or molecule. The reaction often favors formation of the α-glycosidic bond as shown due to the anomeric effect. Peptides with this type of linkage were initially isolated from proteins in human urine and erythrocytes bound to glucose oligosaccharides.
A strong covalent bond between amino acids that functions in maintaining a. The glycosidic bond of maltose is formed between the OH of carbon 1 and carbon 4 of 2 glucose monomers. Glycosides may be categorized according to elements involved in the chemical bond.
Glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond. The major glycoprotein of erythrocyte membranes contains many oligosaccharides with the following structure Winzler 1969. It occurs in cells as a breakdown product of starch.
They are formed as a result of a chemical reaction that may be reversible or irreversible. It is a type of covalent bond. A substance in this case an enzyme that speeds up a chemical reaction.
As well as polysaccharides. There are different forms of the glycosidic bond. These are the covalent bonds formed as a result of electron sharing among two or more atoms.
Therefore it forms an alpha 1 4 glycosidic bond. There are are two types of glycosidic bonds - 14 alpha and 14 beta glycosidic bonds. The breakage of a glycosidic linkage by the addition of a water molecule and the action of a catalyst.
A A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate sugar molecule to another group which may or may not be another carbohydrate. In glycogen glucose molecules are attached one after the other by alpha-14 linkages. However in order to make glycogen more compact for storage branch points are created to created links between many shorter glucose polysaccharides.
Glycosidic bonds are covalent bonds used to link a sugar molecule to an -OR group. Which of the following molecules contains a glycosidic linkage type of covalent bond. Thus the name O-glycosidic bond.
Up to 10 cash back Alpha-16 linkages. Glucose and ethanol combine to form ethyl glucoside and water. Likewise S-glycosidic bonds are observed in thioglycosides where sulfur atom bonded as opposed to air in glycosidic.
A reaction that forms a covalent bond between two. It is commonly called malt sugar. In the past three decades many studies have indicated that most polysaccharides isolated from higher plants that displayed immunomodulatory and anticancer activities mainly present as glucans with varying glycosidic linkage on their main-chain.
Glucose and ethanol combine to form ethyl glucoside and water. The -OR group can be a sugar molecule or non-sugar molecule. C-glycosyl bonds possess glycosidic.
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate sugar molecule to another group which may or may not be another. Formation of ethyl glucoside. Similarly an ionic bond is formed between a positively charged and.

Glycosidic Linkage Definition Overview Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Glycosidic Bonds Labster Theory
Difference Between Glycosidic Bond And Peptide Bond Definition Formation Properties

Glycosidic Linkage Definition Overview Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
0 Comments